Maven artifacts
Maven is a build tool to manage Java, Kotlin and Scala projects (or other similar JVM based languages) and artifacts.
Bytesafe private Maven registries allow users to both deploy internal Maven artifacts and proxy public packages from Maven repositories. A single source for all Maven compatible packages required by your teams and CI/CD pipelines.
For detailed download and instructions on how to use Maven, see the official Apache Maven docs.
Bytesafe is also compatible with Gradle.
Did you know you can get copy-paste ready instructions directly in Bytesafe?
Contextual according to the registry. Login to Bytesafe and select More Info for the registry of your choice.
Configuring Maven to access Bytesafe
To get started create a private Maven Firewall registry, an access token and configure Maven.
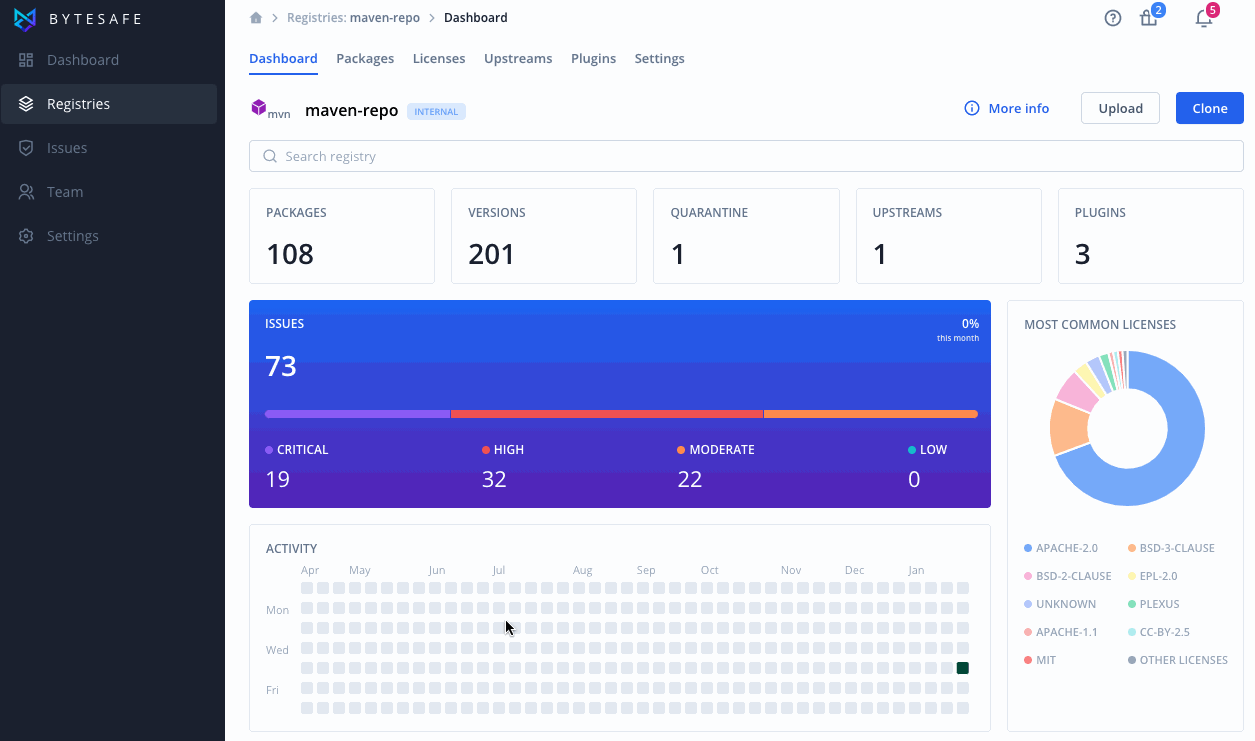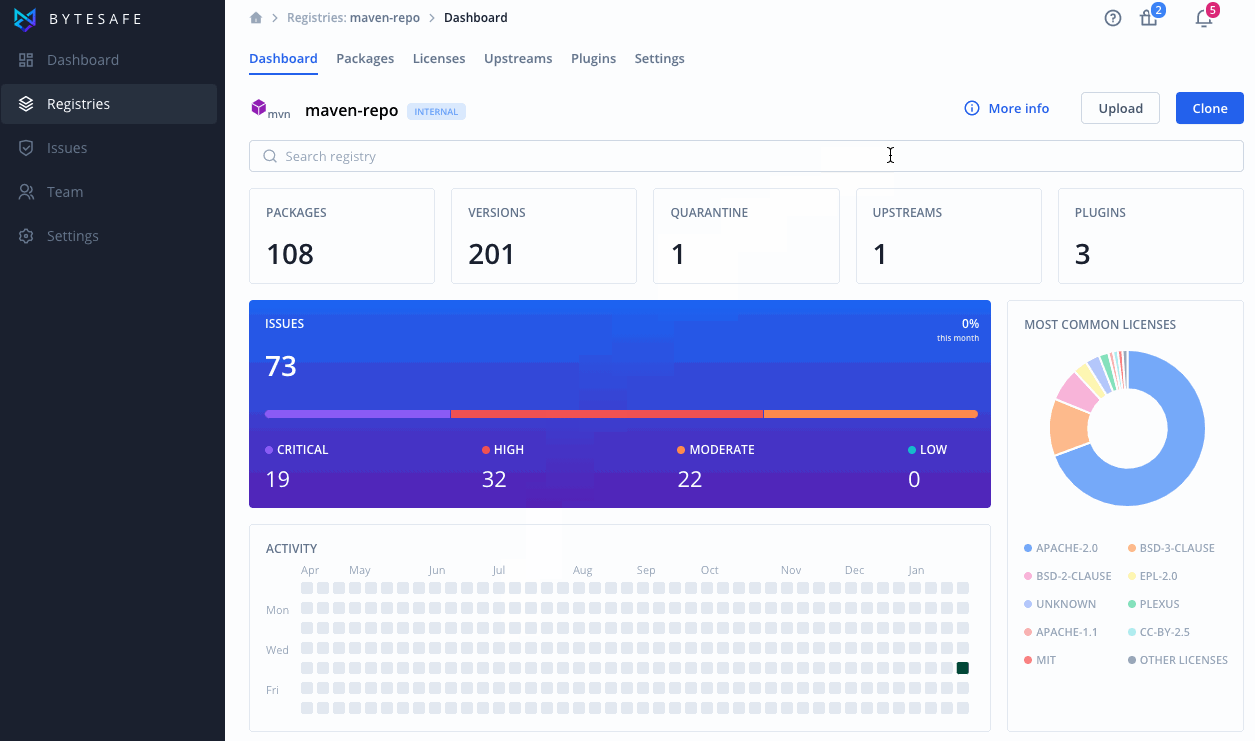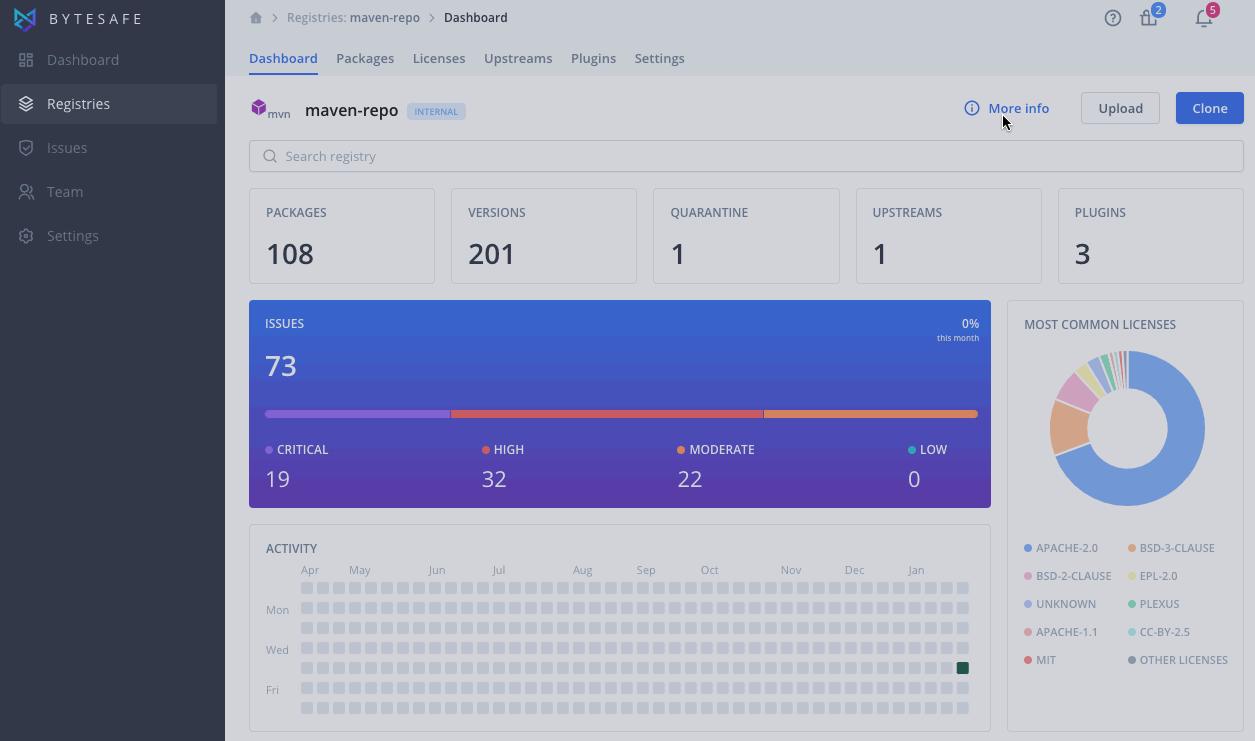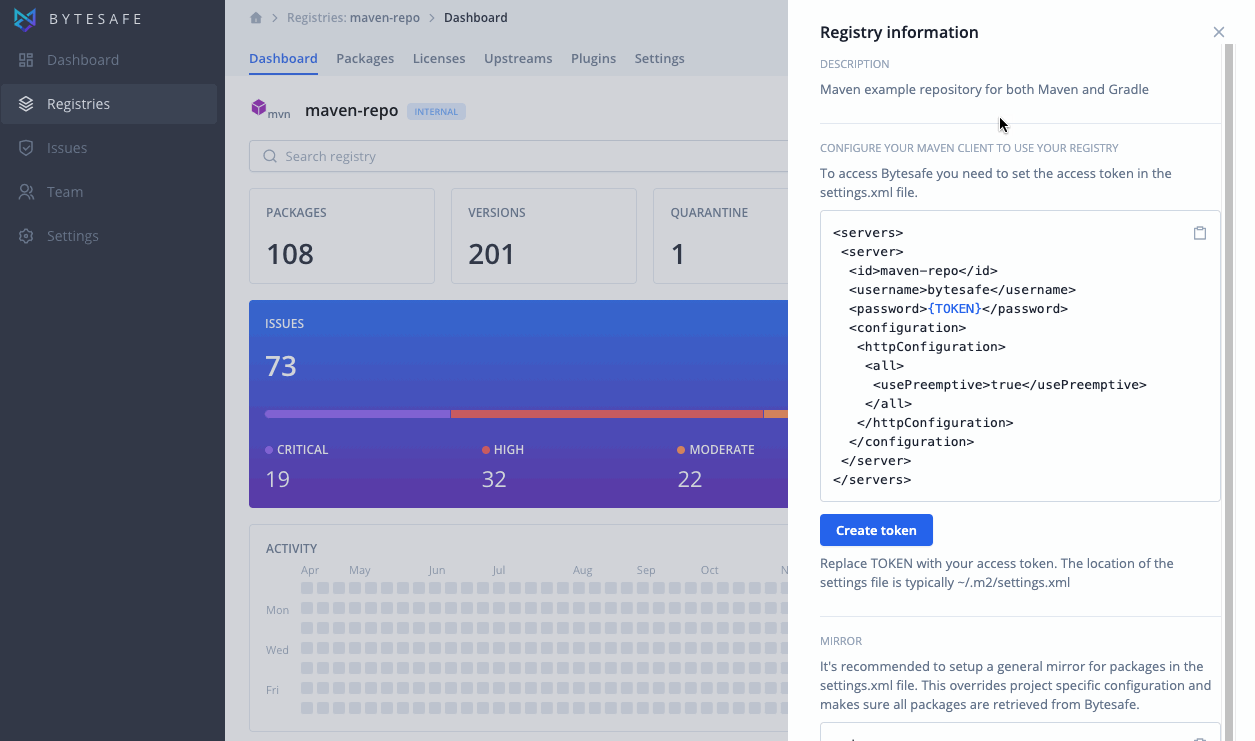
To use Maven with Bytesafe users need to add an access token.
Add the configuration to your settings.xml configuration file (typically, ~/.m2/settings.xml). See the Maven documentation for more information.
Clear the local Maven cache
Before you start it’s always a good idea to clear the local cache in order to ensure Maven installs packages from Bytesafe. Simply delete your ~/.m2/repository directory.
# Install Maven dependencies from Bytesafe
$ rm -rf ~/.m2/repository
Access token in settings.xml
<!-- Add the access token and id configuration to settings.xml -->
<servers>
<server>
<id>{MAVEN-REGISTRY}</id>
<username>{USER}</username>
<password>{ACCESS-TOKEN}</password>
<configuration>
<httpConfiguration>
<all>
<usePreemptive>true</usePreemptive>
</all>
</httpConfiguration>
</configuration>
</server>
</servers>
Note: id value needs to match other configuration like Mirrors, Repositories etc.
To avoid authentication errors, preemptive Authentication (<usePreemptive>) should be set to true.
Create a Maven access token
Maven registries in Bytesafe are private and only available to users with a secure access tokens.
Create an access token in Bytesafe by selecting Access tokens from the profile menu.
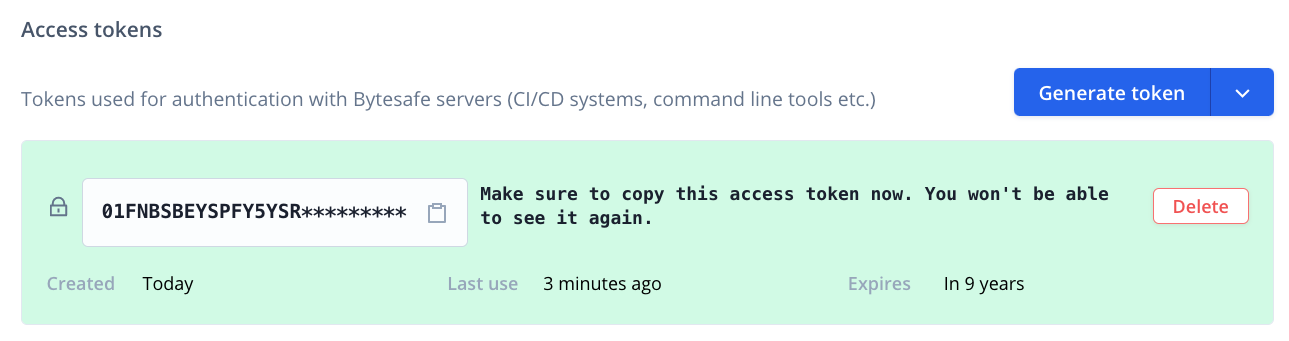
For security reasons the full token is only available upon creation.
Mirror
Maven separates infrastructure configuration (settings.xml) and project level configuration (pom.xml).
It’s recommended to setup a general mirror for packages in the settings.xml file. This overrides project specific configuration to retrieve packages from Bytesafe, to make sure security features in Bytesafe are not bypassed for individual projects.
Mirror configuration in settings.xml
<!-- Add the access token and id configuration to settings.xml -->
<mirrors>
<mirror>
<id>{MAVEN-REGISTRY}</id>
<mirrorOf>*</mirrorOf>
<url>https://{WORKSPACE}.bytesafe.dev/maven/{REGISTRY}/</url>
</mirror>
</mirrors>
The <id> value should match the server configuration to match the access token.
Setting <mirrorOf>*</mirrorOf> results in the mirror being used to retrieve all release versions of packages (including plugins).
For snapshot versions, see installing maven snapshots.
Example: Use case where Bytesafe registry is used as a mirror, and the public Maven Central repository is configured as an upstream. Bytesafe will proxy public dependencies and pull any required version into Bytesafe.
For users that require multiple package sources, mirrors can also be configured to handle multiple repositories. See alternative mirror setup for more details.
For more advanced information on mirror settings, refer to mirror settings in the Apache Maven docs.
Deploy / Upload Maven artifacts
Maven artifacts can be added to Bytesafe either using mvn deploy or by uploading files manually in Bytesafe.
To deploy using mvn users need to add the necessary configuration to the project pom.xml file.
See the registry information in Bytesafe for workspace specific instructions.
DistributionManagement in pom.xml
<!-- Add the repository and snapshotRepository configuration to pom.xml -->
<distributionManagement>
<repository>
<id>{MAVEN-REGISTRY}</id>
<url>https://{WORKSPACE}.bytesafe.dev/maven/{REGISTRY}/</url>
</repository>
<snapshotRepository>
<id>{MAVEN-REGISTRY}</id>
<url>https://{WORKSPACE}.bytesafe.dev/maven/{REGISTRY}/</url>
</snapshotRepository>
</distributionManagement>
With your Maven project sucessfully configured and a valid access token added to settings.xml you can deploy artifacts to Bytesafe.
# Deploy artifacts to Bytesafe using Maven
$ mvn clean deploy
Artifacts are available in Bytesafe as soon as the upload is finalized.
Install Maven dependencies
Maven dependencies are specified with <dependency> in the pom.xml file. If required, copy-paste ready version specific instructions are available on any package version page in Bytesafe.
Dependencies in pom.xml
<!-- Add dependencies be specifying them in the pom.xml file -->
<dependency>
<groupId>{GROUP_ID}</groupId>
<artifactId>{ARTIFACT_ID}</artifactId>
<version>{PACKAGE_VERSION}</version>
</dependency>
With project dependencies specified in the pom.xml file (using valid settings.xml), you can install dependencies using regular Maven commands like mvn install or mvn verify.
# Install Maven dependencies from Bytesafe
$ mvn clean install
With a public repository like Maven Central as an upstream for a registry, Bytesafe will proxy public dependencies and pull any required version into Bytesafe.
Installing SNAPSHOT versions
To install snapshot versions (X.-SNAPSHOT) with Maven, users are required to explicitly specify the use of a snapshot repository.
This is because there is no default snapshot repository in Maven.
Snapshot repository configuration in pom.xml
<!-- Snapshot repository configuration in pom.xml -->
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>{MAVEN-REGISTRY}</id>
<url>https://{WORKSPACE}.bytesafe.dev/maven/{REGISTRY}/</url>
<releases>
<enabled>true</id>
<updatePolicy>always</url>
</releases>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</id>
<updatePolicy>always</url>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
Users that prefer project agnostic snapshot settings can alternatively configure snapshot repositories as part of their profile in settings.xml.
Proxy Maven Central as an upstream
Proxy public Maven dependencies with Bytesafe by adding a public Maven repository as an upstream for a registry.
To add an upstream source, go to the upstreams tab for a registry and click Add upstream button.
In the sidebar, select the public repository, Maven Central or select External URL in the drop-down list.
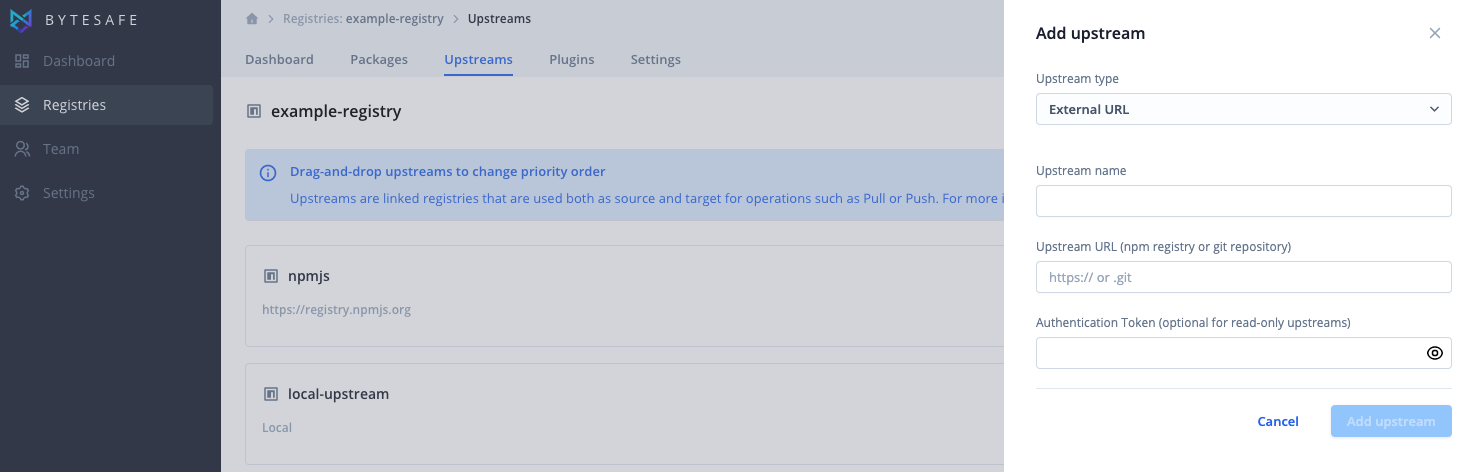
No additional information is required to pull packages from the Maven Central. Users that also want to push packages are required to provide their authentication token.
To use another external repository instead, provide the URL and any required credentials.
Actions related to enabled plugins (like vulnerability scanning and license compliance checks) are performed before package versions enter Bytesafe.
Maven with multiple package sources
There are multiple ways to configure Maven depending on the use case. Users that require multiple package sources or want to use Bytesafe solely for private dependencies can opt to not provide a general Mirror that directs download traffic to Bytesafe.
Available options:
- Alternative mirror setup (excluding select repositories)
- Add multiple upstream sources for a registry
- Provide project level configuration for package
repositoryin thepom.xmlfile
Alternative mirror setup
Mirror settings can manage multiple repositories and can also be used to exclude select repositories from a specific mirror.
The value assigned to <mirrorOf> defines what use case or repository a mirror will be used for.
Examples:
- * = everything*
- central = Maven Central repository
- external: = everything not on the localhost and not file based.*
- repo,repo1 = repo or repo1
- *,!repo1 = everything except repo1
Users that want to use multiple mirrors should consider using at least one mirror with *,!repo1 or providing a mirror configuration for central to proxy and retrieve any missing public packages through Bytesafe.
For more advanced information on mirror settings, refer to mirror settings in the Apache Maven docs.
Add multiple upstream sources for a registry
Users may want to separate release and snapshot versions in individual Bytesafe registries when deploying packages.
To avoid multiple mirror configurations, one option is to use upstreams to use multiple package sources with a single configuration.
By setting upstreams like:
- release version registry (for release versions)
- snapshot version registry (for snapshot versions)
- Maven central (for public dependencies + plugins)
Maven will be able to retrieve all the required packages for an installation without using multiple repository sources.
Provide project level configuration for package repository
Migrating individual projects to Bytesafe it may be beneficial to a local configuration for Maven.
Local configuration is stored under .mvn folder for a project.
Local config can contain mirror and other settings compared to the regular infrastructure settings.
# A maven.config file is used to direct to the local settings file
$ cat .mvn/maven.config
-- settings ./.mvn/local-settings.xml
# the local settings file contain the local settings
$ cat .mvn/local-settings.xml
...
Using Bytesafe together with an internal repository
In certain situations it may not be acceptable to connect to sources outside of the internal network for security reasons. In such environments, it is desirable to set up an internal repository to house a copy of artifacts, and to publish private artifacts to, while simultaneously using Bytesafe as a secure source for external dependencies.
See Maven docs on using an internal repository for more information.
Gradle configuration
Gradle is build automation tool for building JVM-based projects that works with Maven compatible repositories.
To resolve project dependencies from Bytesafe a Bytesafe Maven repository needs to be declared in the build.gradle file.
For details how to configure the build.gradle file, look at this example in the Gradle documentation How to build a Java Library Sample using Gradle, but remember to replace Maven Central configuration with Bytesafe, based on the example below.
./gradlew init starts a step-by-step guide where you can create a library or application with a simple project structure.
Using Gradle to install a package
When you’ve configured Gradle to use Bytesafe, run ./gradlew build to build your project and install dependencies from Bytesafe.
// repository configuration in build.gradle
repositories {
maven {
name = 'bytesafe'
url 'https://{WORKSPACE}.bytesafe.dev/maven/{REGISTRY}/'
credentials {
username = 'bytesafe'
password = '{ACCESS-TOKEN}'
}
}
}
// specify project dependencies
dependencies {
implementation '{GROUP_ID}:{ARTIFACT_ID}:{VERSION}'
}
~/.gradle/gradle.properties file to avoid unintended distribution of credentialsRefresh dependencies
To make sure you don’t use the local cache you might need to --refresh-dependencies when building with ./gradlew build --refresh-dependencies the project to ensure packages are fetched from Bytesafe.
You can choose to delete the local gradle cache by deleting files under ~/.gradle/caches (or %USERPROFILE%\.gradle\caches on Windows).
Using Gradle to publish a package
To publish a package enable the maven-publish plugin, specify the target publishing repository in build.gradle file and use the Gradle command ./gradlew publish.
For more details, see the Maven Publish Plugin in the Gradle documentation.
When you’ve configured Gradle to publish artifacts to Bytesafe, run ./gradlew publish to build your project and upload your artifact to Bytesafe.
publishing {
plugins {
id 'maven-publish'
}
publications {
maven(MavenPublication) {
groupId = '{GROUP_ID}'
artifactId = '{ARTIFACT_ID}'
version = '{PACKAGE_VERSION}'
from components.java
}
}
repositories {
maven {
name = 'bytesafe'
url = 'https://{WORKSPACE}.bytesafe.dev/maven/{REGISTRY}/'
credentials {
username = 'bytesafe'
password = '{ACCESS-TOKEN}'
}
}
}
}
For information on how to set up a Gradle project, see the official Gradle docs.